9. Backups Management¶
Table of contents
9.1. Introduction¶
Backing up your data is an essential part of any IT infrastructure. In the new Cloud Services Portal, we offer you various options for reliably backing up your important data in virtual machines (VMs) and volumes and restoring it if necessary.
With the new backup function in the Cloud Services Portal, we provide you with a modern and user-friendly solution that has been specially developed to:
- Ensure maximum data security through block-based backups.
- Simplify and speed up the recovery process.
- Enable automated and scheduled backups.
- Provide protection against ransomware through strict backup policies.
- Enable storage flexibility through local and external backup options.
This documentation guides you through all the important aspects of the backup function and shows you how to protect your data in the best possible way.
9.2. An overview of the backup options¶
To make it easier for you to choose, we have compiled a comprehensive overview of all available backup solutions in our Cloud Services Portal. Each solution has its own specific strengths and is suitable for different use cases.
| Function | Portal Backup | Restic |
|---|---|---|
| Basic properties | ||
| Type | block-based | file-based |
| Atomar (live backup) | Yes | No |
| Incremental | Yes (CoW) | Yes |
| Memory optimization | ||
| Compression | No | Yes |
| Deduplication | No | Yes |
| Encryption | Yes | Yes |
| Location | ||
| Local storage (AZ) | Yes (CoW) | Yes |
| External memory | Yes (rbd-mirror+CoW) | Ja (object-storage) |
| Security functions | ||
| Deletion protection | Yes | No |
| strict backup policies | Yes | No |
| Supported resources | ||
| Attached volumes | Yes | Yes |
| Volume-based VM | Yes | Yes |
| Image-based VM | Yes | Yes |
| Image VM (local storage) | No | Yes |
| Restore options | ||
| Restore as a new volume | Yes | Yes |
| Restore as new VM | Yes | Yes |
| In-Place Recovery Volume | Yes | Yes |
| In-place recovery VM | Yes | Yes |
| Restoration in another AZ | Yes | Yes |
| Advanced functions | ||
| Consistency groups | In the next version | No |
| Continuous data protection | In the next version | No |
Note
- CoW = Copy-on-Write technology
- AZ = Availability Zone
9.2.1. Recommendations for selection¶
- Portal Backup: Best choice for mission-critical workloads with high security requirements
- Restic: Recommended for special use cases with a need for file-level backups
Tip
The portal backup offers the most comprehensive functions and is particularly recommended for productive environments that place high demands on data security and recoverability.
9.3. Manage backup policies¶
Backup policies are the heart of our backup solution. They define:
- When a backup is created.
- How often backups are created.
- How long backups are stored.
- how to handle errors.
A well thought-out backup policy helps to protect your data effectively.
9.3.1. Components of a backup policy¶
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Unique identifier of the backup policy (e.g. “daily-production-backup”) |
| Backup backend rule | Defines the target storage for backups. The robust ‘rbd’ (RADOS Block Device) backend is currently supported |
| Backup strategy | Determines the immutability of the policy:
flexible: Can be modified or removed
strict: Provides protection against unintentional changes or manipulation
|
| Backup time window | Maximum random delay (in hours) before the backup is created.
Prevents load peaks through simultaneous backup starts
|
| Description | Detailed, comprehensible description of the backup purpose and configuration |
| Incremental policy | Number of incremental backups between full backups.
Optimizes storage usage and backup speed
|
| Notification e-mail | E-mail address for status messages after backup execution |
| Storage in primary storage | Number of backup generations to be kept locally.
Enables fast recovery
|
| Storage in secondary storage | Number of backup generations to be stored externally.
Ensures additional data security
|
| Repeats | Maximum number of retries for failed backups.
Increases the reliability of the backup process
|
| Schedule | Defines the backup frequency:
Daily: For critical productive data
Weekly: For rarely changing data
Monthly: For archiving purposes
|
Note
The combination of these properties allows you to precisely coordinate your backup strategy. Please note the following aspects when configuring your policies:
- Datasecurity
- Resource usage
- Restoration times
Tip
We recommend for critical production systems:
- stict Backup policies to protect against accidental changes
- Short backup intervals (daily)
- Sufficient storage time in both storage levels
- Enabled e-mail notifications for prompt response to problems
9.3.2. Available backup policies¶
| Name | Backend rule | strategy | Time window | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| relaxed-daily-7 | rbd | flexible | 4 | 7 flexible daily backups |
| relaxed-daily-21 | rbd | flexible | 4 | 21 flexible daily backups |
| relaxed-daily-35 | rbd | flexible | 4 | 35 flexible backups daily |
Note
Further backup policies such as weekly, monthly and strict will follow shortly.
9.4. Assign backup policy to a resource¶
You can assign backup policies at the following levels:
- Project level The policy set here is adopted dynamically for all underlying VMs.
- VM level The policy set here is adopted for all underlying volumes.
- Volume level The policy set here is only applied to the defined volume.
The levels are managed hierarchically, so definitions at volume level overwrite those at project level.
Warning
As soon as the strict property is set for a backup policy, this policy can no longer be changed.
9.4.1. Best Practices¶
- For dynamic projects with frequent VM creation: Use project-level backup policies
- For static projects: Use VM or volume-level backup policies
9.5. Ransomware protection¶
Important
- strict backup policies prevent ransomware attacks from removing the backup policies
- TTLs can be extended, but never shortened
- TTLs prevent premature backup deletion
9.7. Backup dashboard overview¶
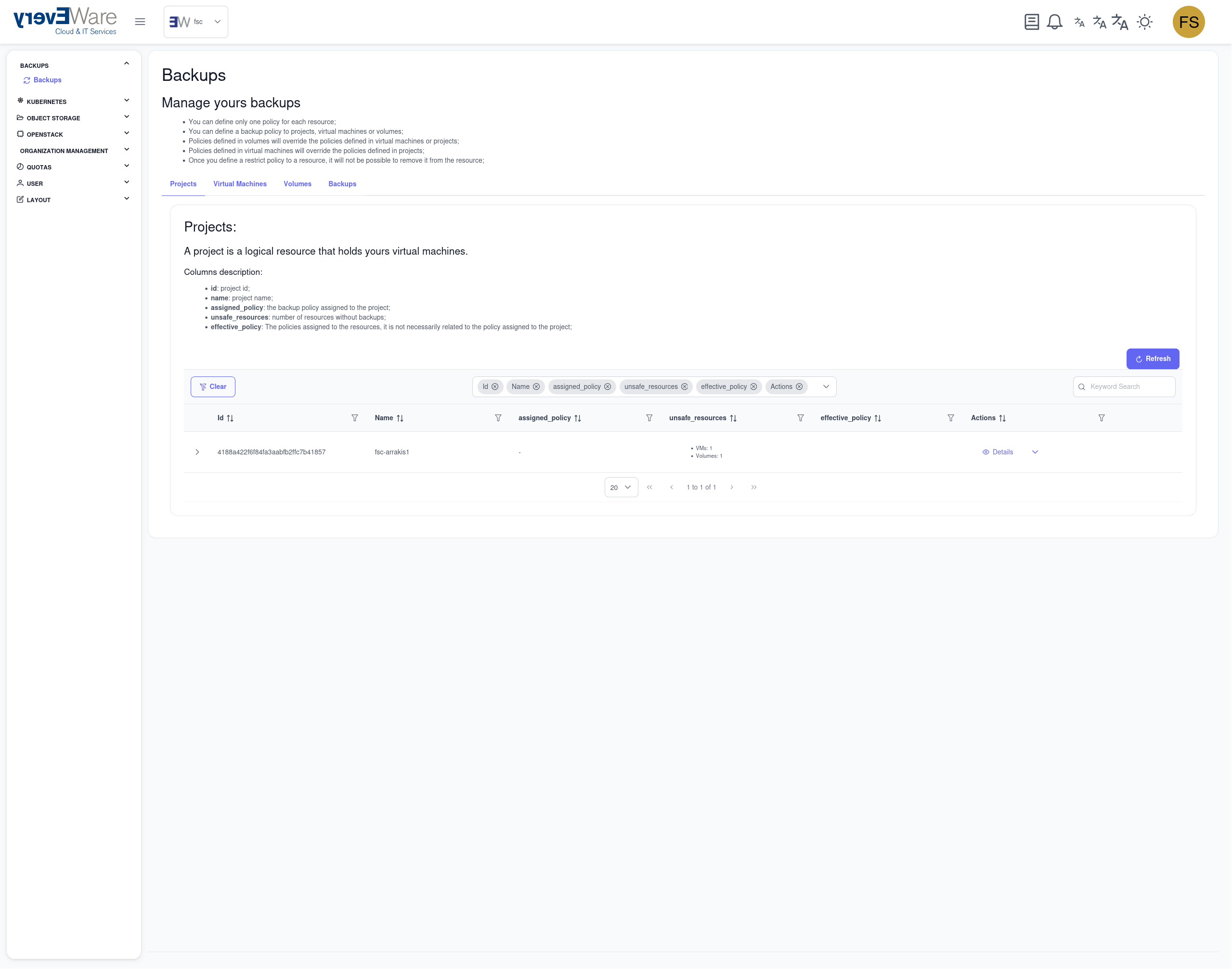
9.7.1. Projects¶
Shows you a list of your available projects On the right-hand side you can:
- Set backup policy: To assign a backup policy at project level
Functions:
- Projects can be expanded to display associated VMs
- VMs can be expanded to display attached volumes (cinder volumes and Nova disk for image-based VMs)
- Volumes can be expanded to view their backups
- Available backup actions are described in the ‘Backups’ section
9.7.2. Virtual machines¶
Shows you a list of your available VMs On the right-hand side, you can:
- Set backup policy: To assign a backup policy at VM level
Functions:
- VMs can be expanded to display attached volumes (cinder volumes and Nova disk for image-based VMs)
- Volumes can be expanded to view their backups
- Available backup actions are described in the ‘Backups’ section
9.7.3. Volumes¶
Shows you a list of your available volumes On the right-hand side you can:
- Set backup policy: To assign a backup policy at the volume level
Functions:
- Volumes can be expanded to view their backups
- Available backup actions are described in the ‘Backups’ section
9.7.4. Backups¶
Here you will find an overview of all your backups:
9.7.4.1. Available backups¶
Shows all completed, non-expired backups. Available actions:
- Details: Show all information about the backup
- Extend backup lifetime: Extend TTL of the backup, e.g. for longer-term storage of year-end backups; unlimited storage possible
- In-place restore: Restore to a (unmounted) volume or a (shutdown) VM
- Restore as new volume: Restore to a new volume (name, AZ and volume type required)
- Restore as new image: Restore as new Glance image (image name required)
9.7.4.2. Ongoing restorations¶
Shows backups with ongoing recovery.
9.7.4.3. Scheduled backups¶
Shows upcoming scheduled backups. Available actions:
- Details: Show all information about the planned backup
- Run immediately: Create backup manually and immediately
9.7.4.4. Faulty backups¶
Shows backups with restore errors.
9.7.4.5. Expired backups¶
Shows expired backups (deleted from memory). Available actions:
- Details: Show all information about the expired backup
Note
- AZ = Availability Zone
- TTL = Time To Live (Lebensdauer)
- EoY = End of Year
9.8. Step-by-step: Applying a backup policy and performing a restore¶
In this step-by-step guide, we show you how to:
- Apply a backup policy to an image-based VM (e-flavor)
- Execute the backup policy manually to create a backup immediately
- Perform an in-place restore to undo all changes since the backup
Important
- The VM may remain in state active during backup creation.
- The VM must be in state Shutdown for restore.
9.8.1. 1. apply backup policy to an image-based VM¶
9.8.1.1. First steps¶
Navigate to the “Backups” section in the portal via the left sidebar:
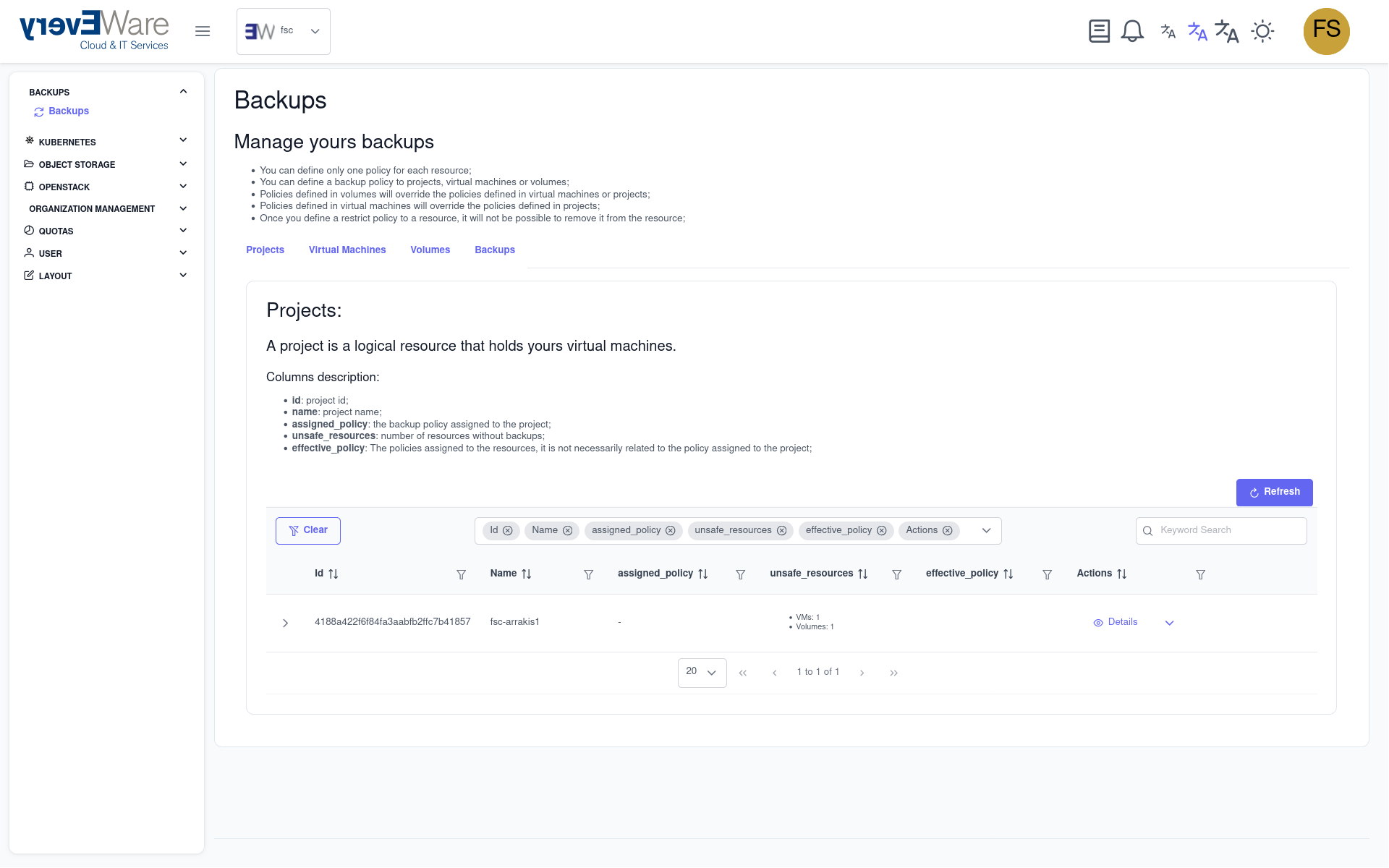
- Switch to the VM overview:
- Click on the “Virtual machines” tab
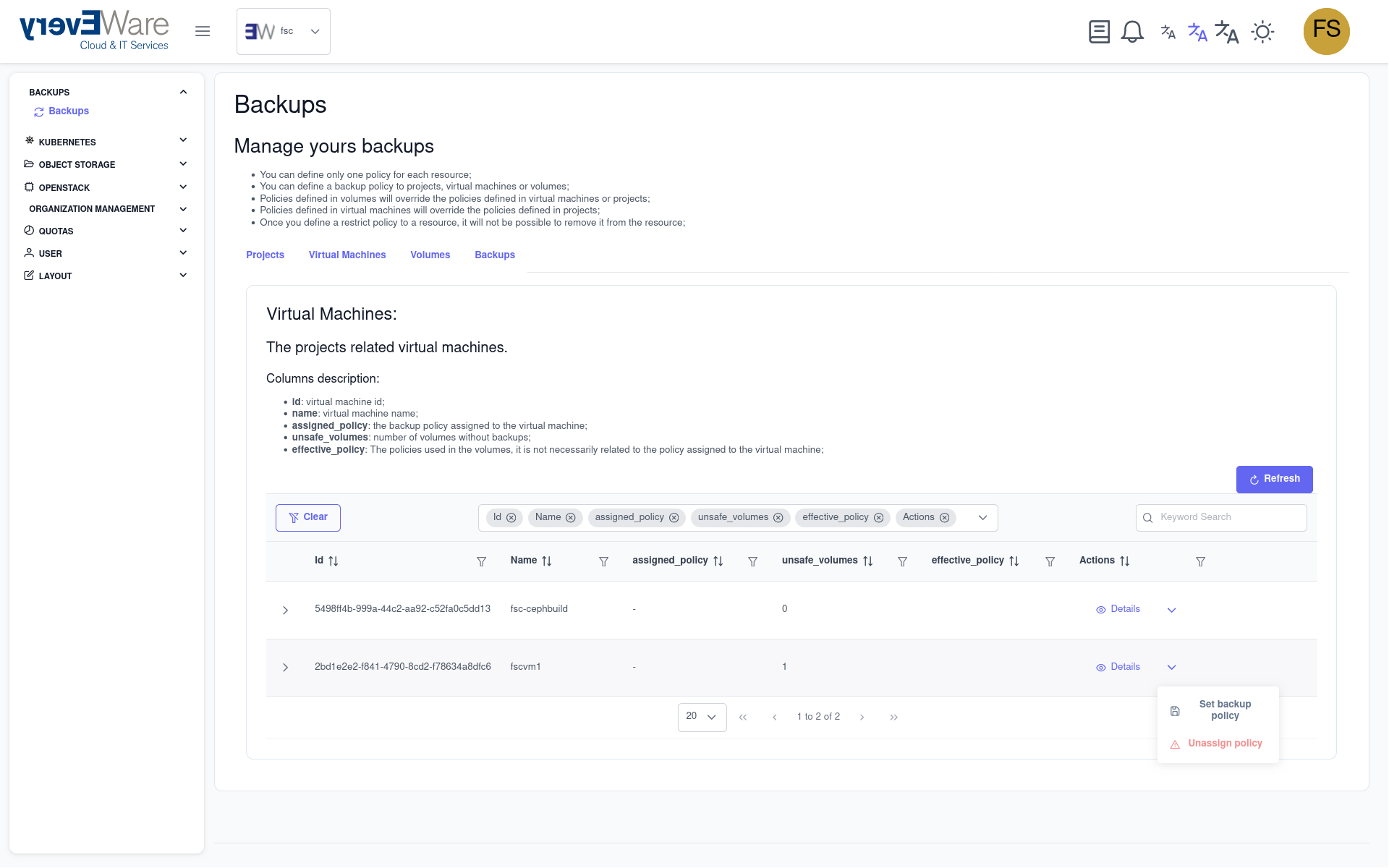
- Assign backup policy:
- Click on “Set backup policy” in the action column on the right
- Select the “relaxed-daily-7” policy
- Enter “2” as the start time
- Click on “Set policy”
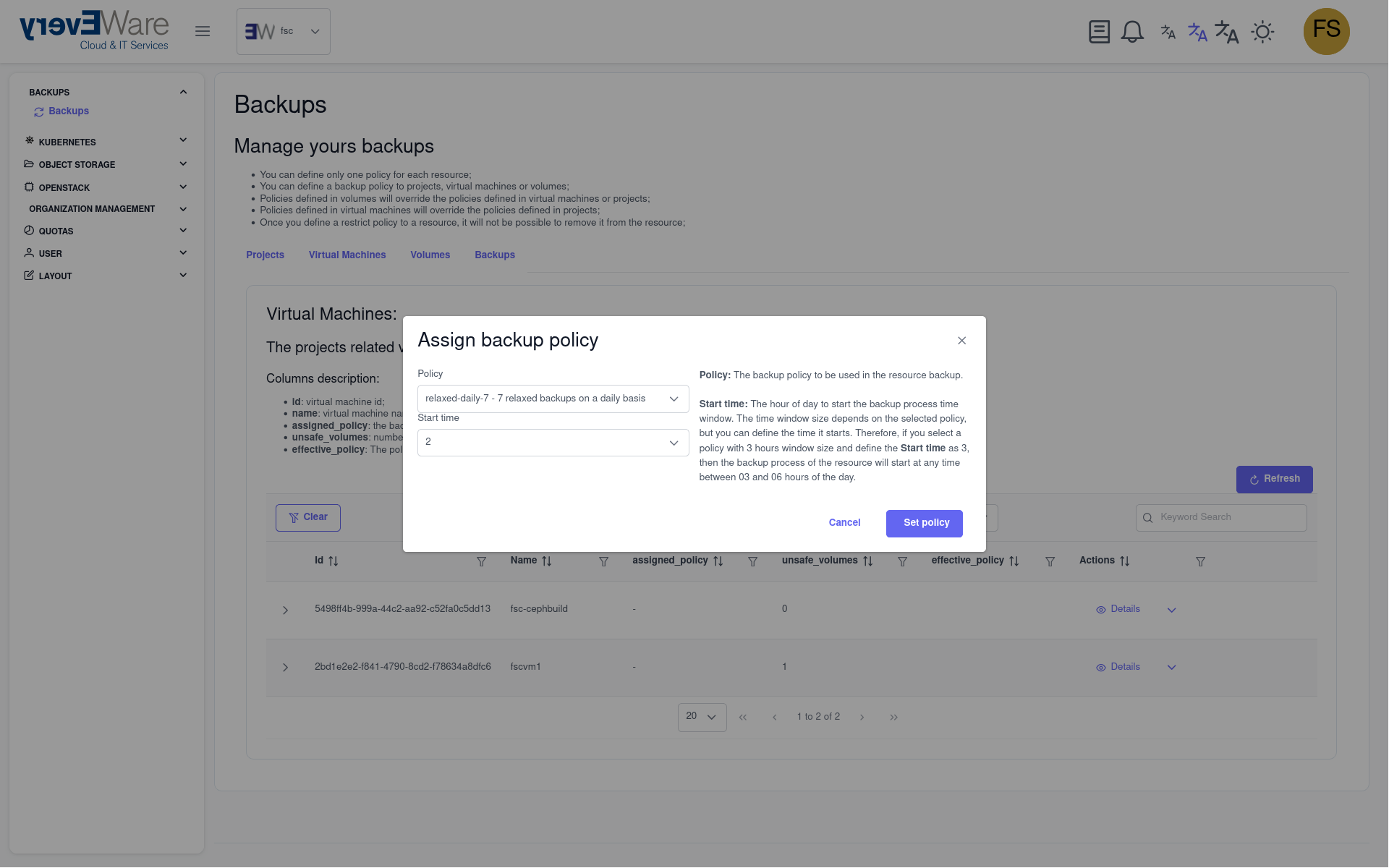
9.8.2. 2. execute backup immediately¶
- Display volumes and switch to the backup plan:
- Click on the expand button on the left to display all volumes of the VM
- Select the “Scheduled backups” tab
- Click on “Execute immediately” in the action column on the right
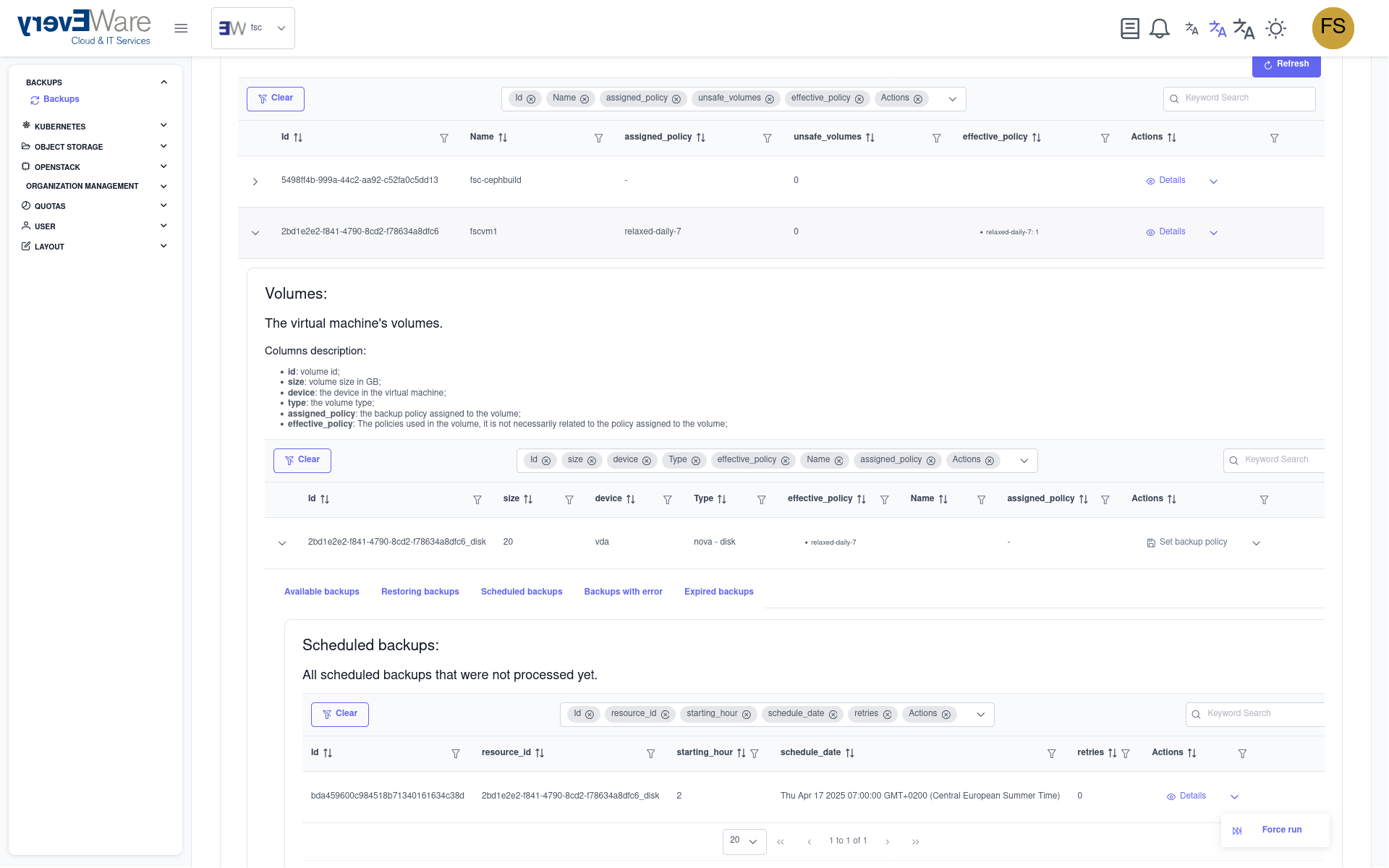
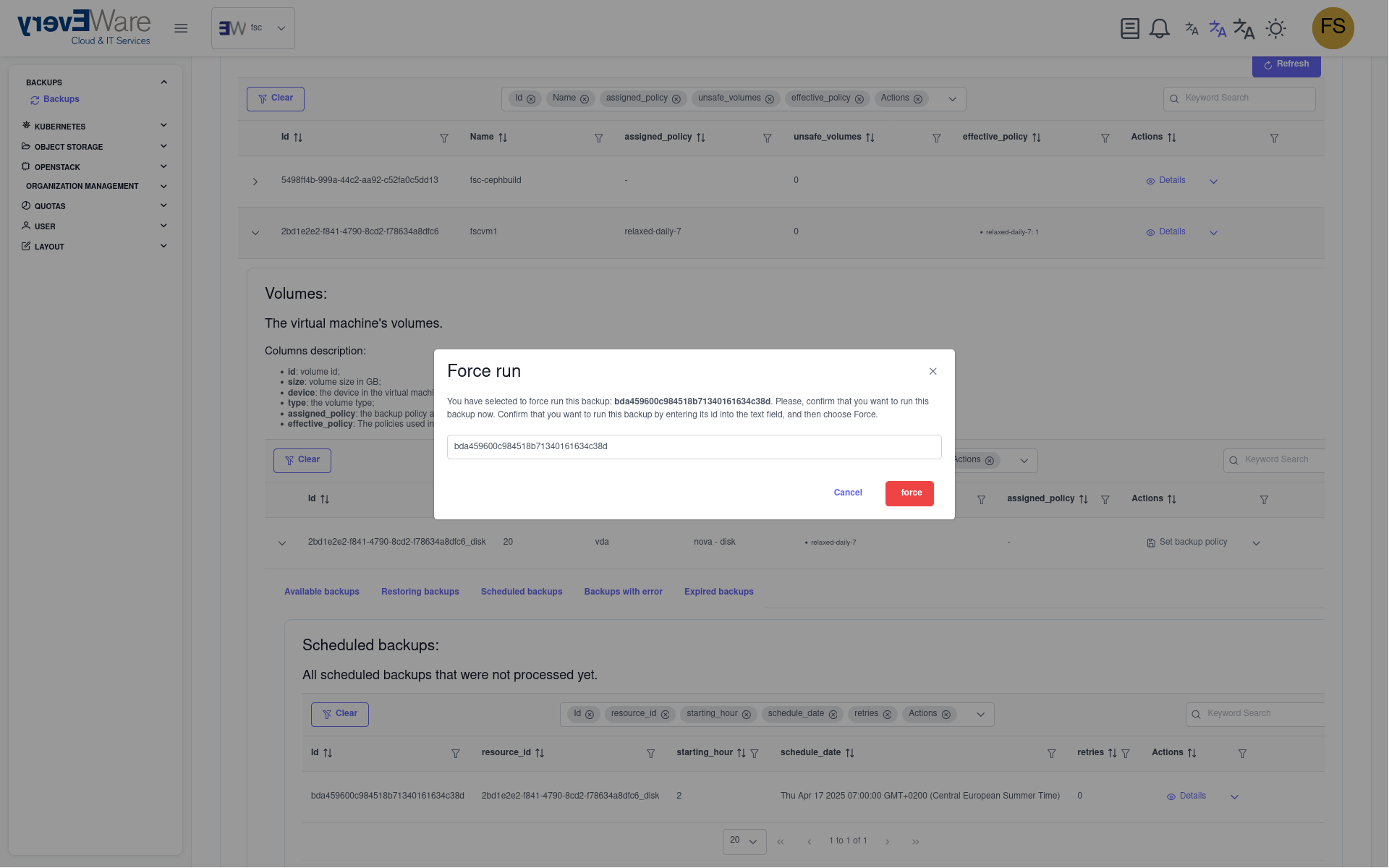
- Start backup:
- Enter the backup ID
- Click on “Execute”
9.8.3. 3. perform an in-place restore¶
- Restore backup:
- Navigate to the “Backups” area
- Select the “Available backups” tab
- Wait until the new backup is available
- Click on “In-place restore” in the action column on the right
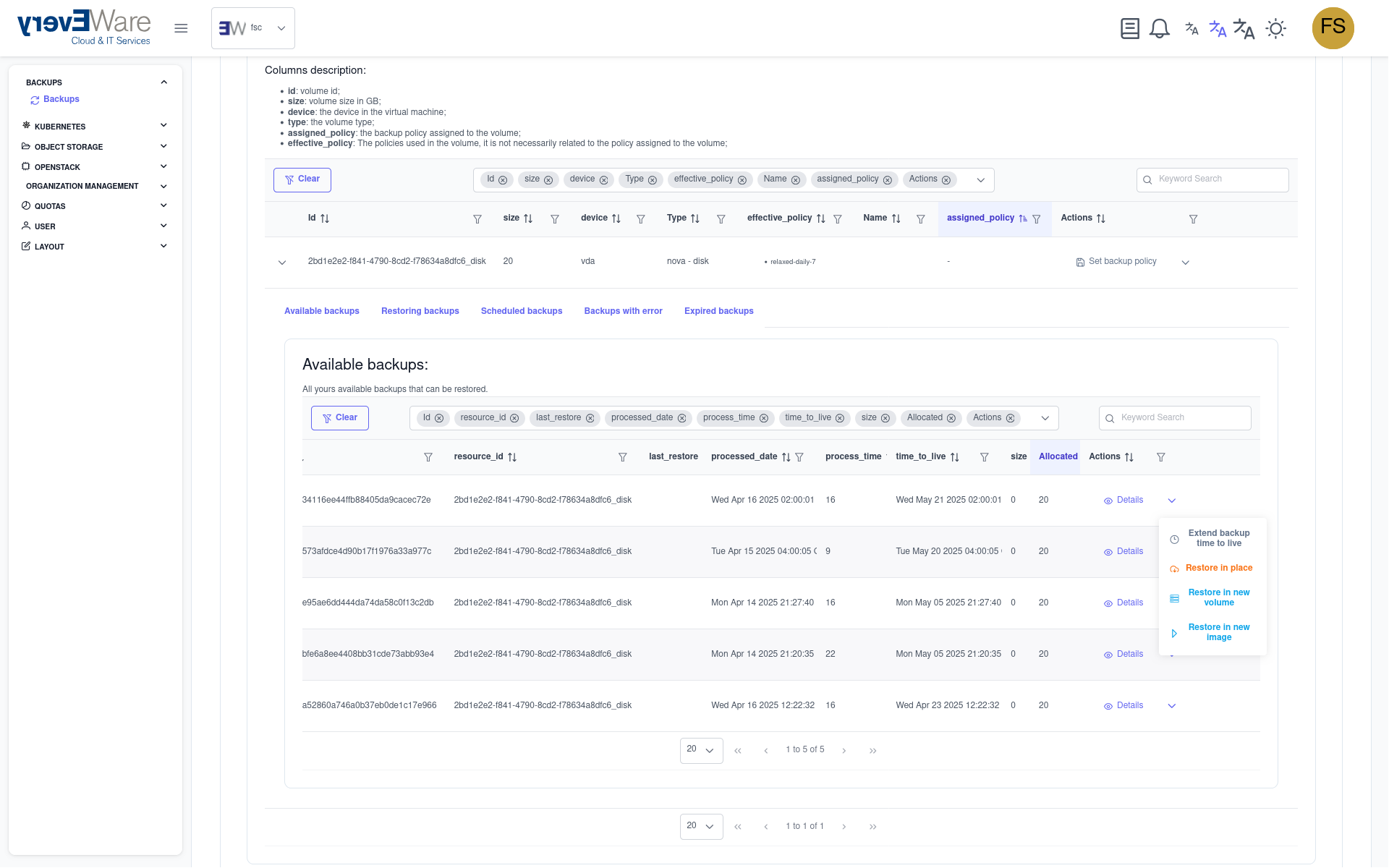
- Confirm restoration:
- Enter the backup ID
- Click on “Restore”
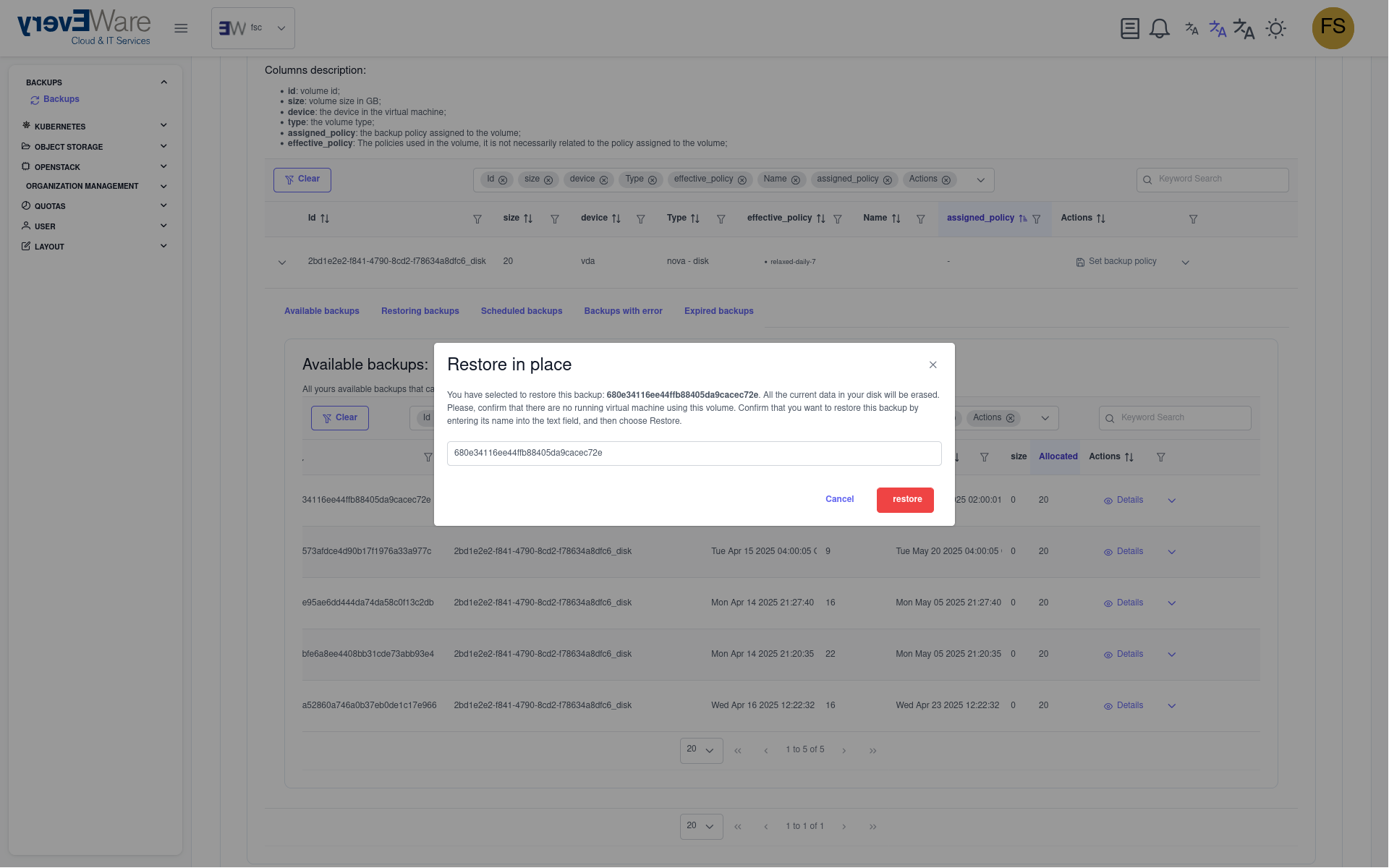
Note
- Ensure that the VM is in state shut down before restoring
- Back up important data before restoring
- You can find the backup ID in the overview of available backups